Touchscreens
Multi- and single-touch screens
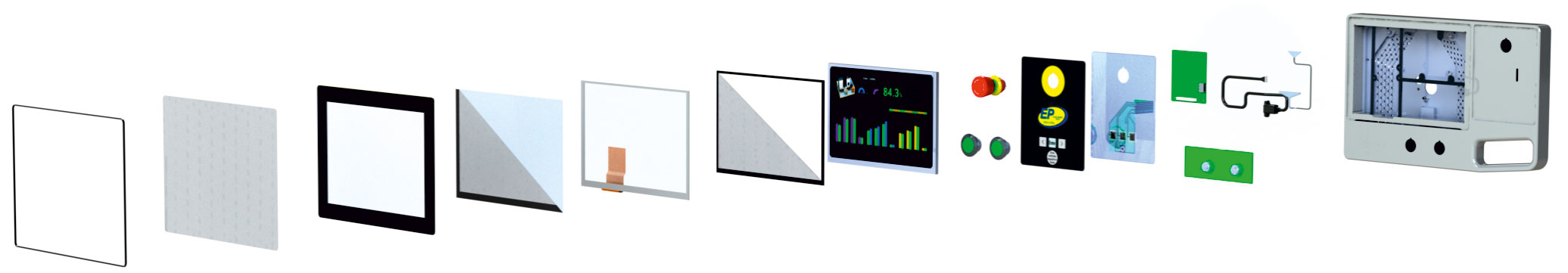
Thanks to our high level of vertical integration and our efficient supplier network, we can offer you the right supply chain solution for every project volume. Our portfolio ranges from classic front foils and membrane keypads to multi-touch display panels or plug&play-capable web panels. Contact us, we will be happy to support you in the realization of your Human Machine Interface (HMI) project.
Click on the respective icon at the top of the graphic to find out more about the individual component!
The joints or edges between two visible parts are particularly susceptible to the ingress of dirt, dust and external media. By potting these joint edges flush with the surface, the ingress of foreign bodies and substances can be effectively prevented. This not only ensures a clean and durable connection, but also enables a higher IP protection class to be achieved, which significantly increases resistance to environmental influences.
The anti-splinter film provides effective protection for glass front panels by preventing the glass from breaking and retaining dangerous splinters. This film not only increases safety, but can also significantly improve the shatter resistance of glass surfaces. In addition, it helps to reduce UV rays, which protects the interior from discoloration.
Glass fronts on HMIs offer a modern and user-friendly surface that is both aesthetically pleasing and functional. They provide a clear view of displays while protecting them from dust and dirt. They are also easy to clean and contribute to the longevity of the device.
Front or decorative foils for HMIs offer a flexible and cost-effective solution for the user interface of devices. They are lightweight and can be produced in different designs and colors to enhance the user experience. In addition, films are resistant to environmental influences, which increases their longevity and functionality.
LOCA Bonding (Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive) is an advanced technology that enables a virtually bubble-free bond between displays and protective glass. By using liquid adhesive, excellent light transmission is achieved, which significantly improves image quality. This method also provides additional protection against shocks and vibrations, increasing the longevity of the devices.
OCA Bonding (Optically Clear Adhesive Bonding) is a technique that enables touch sensors and glass or film surfaces to be seamlessly bonded together, resulting in optimum visibility. This method reduces glare and improves colour intensity by minimizing the distance between the sensor and the cover. OCA bonding also provides effective protection against bumps and scratches, which increases the durability of the devices.
Touch sensors are innovative input devices that enable intuitive and user-friendly interaction with digital displays. They respond to touch and gestures, which considerably simplifies and speeds up the operation of devices. With various technologies such as capacitive and resistive sensors, they offer versatile application possibilities in numerous industries.
LOCA Bonding (Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive) is an advanced technology that enables a virtually bubble-free bond between displays and protective glass. By using liquid adhesive, excellent light transmission is achieved, which significantly improves image quality. This method also provides additional protection against shocks and vibrations, increasing the longevity of the devices.
Air Gap Bonding is a bonding technique that creates an airtight connection between a display and a protective layer without the use of optical tape. This method reduces reflections and improves visibility by minimizing the gap between the two surfaces. It also allows for greater flexibility in the design, resulting in slimmer and lighter devices.
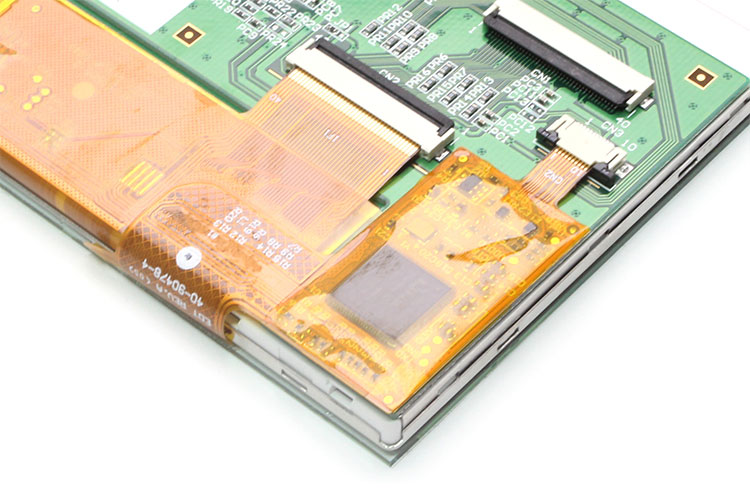
Displays are essential components of modern devices that present information visually and enable user-friendly interaction. They are used in a variety of technologies, such as LCD, OLED and LED, and offer different advantages in terms of image quality and energy efficiency. In addition, displays are available in various sizes and formats to meet the different requirements of applications.
Mechanical buttons are tried-and-tested operating elements that offer a precise and reliable user experience thanks to their tactile feedback. They are widely used in a variety of applications, e.g. in industrial control systems, and impress with their durability and robustness. Thanks to their individual design options, mechanical buttons can be optimally adapted to the specific requirements of the respective device.
The illumination of buttons and logos not only improves visibility in dark environments, but also gives devices an appealing aesthetic. By using LED technology, colors and brightness can be customized to create different user experiences. Illuminated buttons and logos also promote user-friendliness by making interaction more intuitive.
Capacitive buttons use the change in the electrical field to recognize touch, which enables responsive and user-friendly interaction. They offer a modern, elegant design as they are often flush-mounted and have no moving parts. This technology is particularly durable and resistant to wear and tear, which extends the life of the buttons.
Membrane processing for membrane keyboards includes various processes to optimize the functionality and aesthetics of the key surfaces. These include the cutting, printing and laminating of foils, which enable precise adaptation to the respective requirements. These processing techniques not only ensure improved haptics, but also a longer service life and durability of the keys.
Membrane keypads are a versatile and cost-effective solution for operating devices that are characterized by their flat design. They are made of flexible membrane materials that integrate both the keys and the underlying circuitry, which simplifies production. These keyboards offer high resistance to environmental influences, such as moisture and dust, and are therefore ideal for various applications.
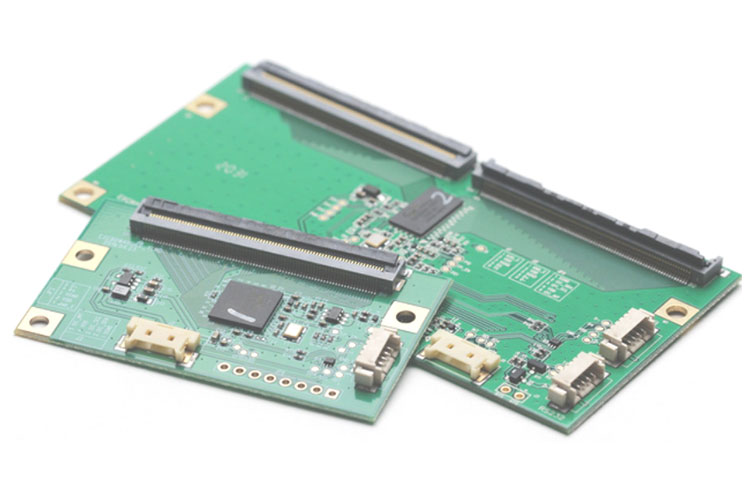
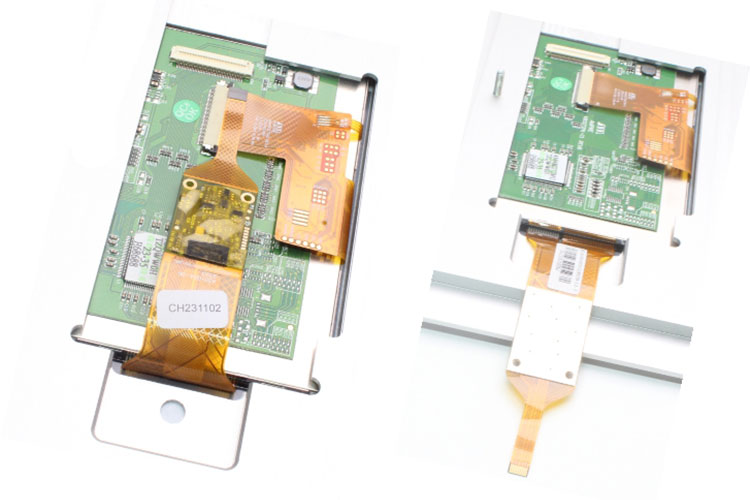
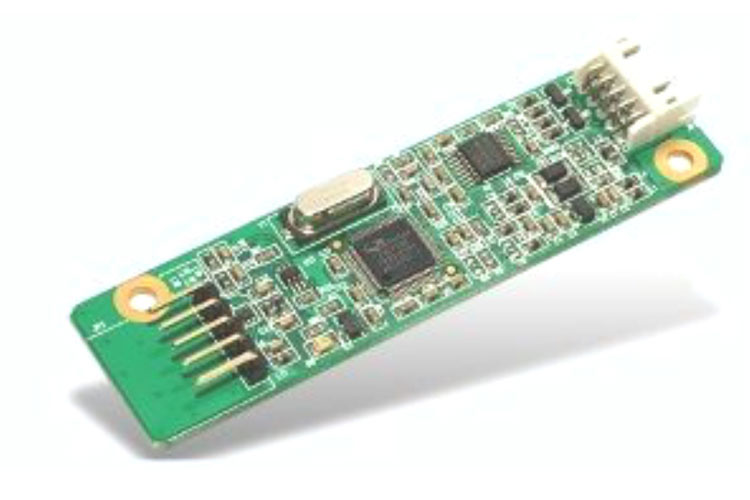
Single board computers are central components in many electronic devices and serve as a platform for processing and controlling information. They integrate important functions such as processors, memory and interfaces to ensure efficient data processing. With their compact design, computer boards are ideal for applications in various industries, from automation technology to portable devices.
The assembly of printed circuit boards is an essential process in electronics production in which electronic components are precisely placed on a printed circuit board (PCB). Techniques such as automated SMD assembly enable fast and efficient placement, ensuring high accuracy and quality. These processes are crucial for the functionality and reliability of electronic devices in various applications.
Cables are indispensable components in electronics that ensure a reliable connection between different devices and systems. They are available in various designs and materials to meet different requirements in terms of current strength, data transmission and environmental conditions. High-quality cables make a decisive contribution to signal quality and the longevity of the entire installation.
Enclosures are crucial components in electronics that not only ensure the protection of internal components from external influences, but also influence the visual design of devices. They are available in various materials, such as metal or plastic, and can be individually designed to meet the specific requirements of a product. Enclosures also contribute to heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding, which increases the performance and reliability of the devices.
Carrier plates are important elements in electronics that serve as a stable basis for the assembly of parts and components. They not only provide structural support, but also help with heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding. With different materials and surface treatments, carrier plates can be adapted to specific requirements and environments.

Gap grouting
The joints or edges between two visible parts are particularly susceptible to the ingress of dirt, dust and external media. By potting these joint edges flush with the surface, the ingress of foreign bodies and substances can be effectively prevented. This not only ensures a clean and durable connection, but also enables a higher IP protection class to be achieved, which significantly increases resistance to environmental influences. Find out more about the advantages and possibilities of gap encapsulation.
Splinter protection film
The anti-splinter film provides effective protection for glass front panels by preventing the glass from breaking and retaining dangerous splinters. This film not only increases safety, but can also significantly improve the shatter resistance of glass surfaces. It also helps to reduce UV rays, which protects the interior from discoloration. More information on the benefits of anti-shatter film and its application.
Glass
Glass fronts on HMIs offer a modern and user-friendly surface that is both aesthetically pleasing and functional. They allow a clear view of displays while protecting them from dust and dirt. They are also easy to clean and contribute to the longevity of the device. Find out more about the possibilities and advantages of glass fronts for HMIs.
Front or decorative films
Front or decorative foils for HMIs offer a flexible and cost-effective solution for the user interface of devices. They are lightweight and can be produced in different designs and colors to enhance the user experience. In addition, films are resistant to environmental influences, which increases their longevity and functionality. More information about the advantages and applications of front or decorative films in HMIs.
LOCA Optical Bonding
LOCA Bonding (Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive) is an advanced technology that enables a virtually bubble-free bond between displays and protective glass. By using liquid adhesive, excellent light transmission is achieved, which significantly improves image quality. This method also provides additional protection against shocks and vibrations, increasing the longevity of the devices. Learn more about the benefits and applications of LOCA bonding.
OCA Bonding
OCA Bonding (Optically Clear Adhesive Bonding) is a technique that allows touch sensors and glass or film surfaces to be seamlessly bonded together, resulting in optimal visibility. This method reduces glare and improves colour intensity by minimizing the distance between the sensor and the cover. OCA bonding also provides effective protection against bumps and scratches, increasing the durability of the devices. Learn more about the benefits and applications of OCA Bonding.
Touch sensor
Touch sensors are innovative input devices that enable intuitive and user-friendly interaction with digital displays. They respond to touch and gestures, which considerably simplifies and speeds up the operation of devices. With various technologies such as capacitive and resistive sensors, they offer versatile application possibilities in numerous industries. Further information about the various touch solutions.
LOCA Optical Bonding
LOCA Bonding (Liquid Optically Clear Adhesive) is an advanced technology that enables a virtually bubble-free bond between displays and protective glass. By using liquid adhesive, excellent light transmission is achieved, which significantly improves image quality. This method also provides additional protection against shocks and vibrations, increasing the longevity of the devices. Learn more about the benefits and applications of LOCA bonding.
Air gap bonding
Air Gap Bonding is a bonding technique that creates an airtight connection between a display and a protective layer without the use of optical tape. This method reduces reflections and improves visibility by minimizing the gap between the two surfaces. It also allows for greater flexibility in the design, resulting in slimmer and lighter devices. More information about Air Gap Bonding and other touch solutions.
Display
Displays are essential components of modern devices that present information visually and enable user-friendly interaction. They are used in a variety of technologies, such as LCD, OLED and LED, and offer different advantages in terms of image quality and energy efficiency. In addition, displays are available in various sizes and formats to meet the different requirements of applications. Learn more about the different display solutions.
Mechanical buttons
Mechanical buttons are tried-and-tested operating elements that offer a precise and reliable user experience thanks to their tactile feedback. They are widely used in a variety of applications, e.g. in industrial control systems, and impress with their durability and robustness. Thanks to their individual design options, mechanical buttons can be optimally adapted to the specific requirements of the respective device. Further information about mechanical buttons and their applications.
Lighting Logo
The illumination of buttons and logos not only improves visibility in dark environments, but also gives devices an appealing aesthetic. By using LED technology, colors and brightness can be customized to create different user experiences. Illuminated buttons and logos also enhance usability by making interaction more intuitive. Find out more about the possibilities of illuminating buttons and logos.
Capacitive buttons
Capacitive buttons use the change in the electric field to detect touch, enabling responsive and user-friendly interaction. They offer a modern, elegant design as they are often flush-mounted and have no moving parts. This technology is particularly durable and resistant to wear and tear, which extends the life of the buttons. Find out more about capacitive buttons and their applications.
Membrane processing
Foil processing for membrane keyboards includes various processes to optimize the functionality and aesthetics of the key surfaces. These include the cutting, printing and laminating of foils, which enable precise adaptation to the respective requirements. These processing techniques not only ensure improved haptics, but also a longer service life and durability of the buttons. More information about foil processing and membrane keyboards.
Membrane keypads
Membrane keypads are a versatile and cost-effective solution for operating devices that are characterized by their flat design. They are made of flexible membrane materials that integrate both the keys and the underlying circuitry, which simplifies production. These keyboards offer high resistance to environmental influences such as moisture and dust and are therefore ideal for various applications. More information about membrane keyboards and their advantages.
Single Board Computer
Single board computers are central components in many electronic devices and serve as a platform for processing and controlling information. They integrate important functions such as processors, memory and interfaces to ensure efficient data processing. With their compact design, computer boards are ideal for applications in various industries, from automation technology to portable devices. Learn more about single board computers and their applications.
Fitting
Printed circuit board assembly is an essential electronics manufacturing process in which electronic components are precisely placed on a printed circuit board (PCB). Techniques such as automated SMD assembly enable fast and efficient placement, guaranteeing high accuracy and quality. These processes are crucial for the functionality and reliability of electronic devices in various applications. Learn more about PCB assembly.
Cables
Cables are indispensable components in electronics that ensure a reliable connection between different devices and systems. They are available in various designs and materials to meet different requirements in terms of current strength, data transmission and environmental conditions. High-quality cables make a decisive contribution to signal quality and the longevity of the entire installation. More information about cables and our comprehensive solutions.
Housing
Enclosures are crucial components in electronics that not only ensure the protection of internal components from external influences, but also influence the visual design of devices. They are available in various materials, such as metal or plastic, and can be customized to meet the specific requirements of a product. Enclosures also contribute to heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding, which increases the performance and reliability of devices. Learn more about enclosures and our comprehensive solutions.
Carrier plates
Carrier plates are important elements in electronics that serve as a stable base for the assembly of parts and components. They not only provide structural support, but also help with heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding. With different materials and surface treatments, carrier plates can be adapted to specific requirements and environments. Learn more about carrier plates and their applications.
Table of contents
Capacitive multi-touch screens - precision and versatility
Capacitive multi-touch screens, also known as CTP (capacitive touch panels), offer a modern, intuitive user experience that is characterized by high precision and responsiveness. They react to electrical changes caused by touching them with a finger, making them easy to operate even with several fingers at the same time (multi-touch). This technology is used in many industrial and medical applications where complex inputs and user interactions are required.

Projective-capacitive touchscreen = multi-touch screen
Multi-touch screen + display = multi-touch display
Advantages of capacitive multi-touch screens
Application examples
Medical technology
Capacitive multi-touch screens are ideal for medical devices where complex inputs need to be made quickly and precisely.
Industrial controls
In automation and production, they enable precise and efficient control of machines.

Surface materials
The surface of capacitive touchscreens is usually made of tempered glass or special composite materials that not only offer excellent scratch resistance, but are also easy to clean. These materials are particularly suitable for environments where hygiene and durability are top priorities.
Resistive single touchscreens - reliability in any environment
Resistive single touchscreens are a proven technology that impresses with its robustness and flexibility. These touchscreens, also known as RTP (resistive touch panels), work on the basis of physical contact between two conductive layers that are pressed together when touched. This means they can be operated with different input devices such as fingers, pens or even gloves, which makes them particularly versatile.
Resistive touchscreen = single touchscreen
Advantages of resistive single touchscreens
Application examples
Industrial applications
In control technology and automation, resistive touchscreens offer a reliable input option, even when used under difficult conditions.
Medical devices
Due to their robustness and operability with gloves, they are particularly suitable for use in medical devices, e.g. patient monitors or infusion pumps.

Surface materials
The surface of resistive touchscreens often consists of flexible polyester on top of a stable glass layer. This combination ensures a durable and resistant surface that works reliably even in harsh or sterile environments. The polyester is easy to clean and resists scratching, making it ideal for industrial and medical applications.
Sensor technology
Functionality of PCAP multi-touch sensors
Capacitive technology
PCAP touchscreens use a thin layer of conductive material such as indium tin oxide (ITO). This layer forms an electric field that changes when touched. This change is recognized and interpreted by a touch controller.
Sensorgrid
The capacitive sensor grid consists of a matrix of electrodes arranged in a grid structure. Each electrode generates an electric field that changes when touched. The exact position and number of contact points are determined by analyzing the capacitance changes in this matrix.
Signal processing
The signals from the electrodes are forwarded to a touch controller, which processes the data and converts it into coordinates that are interpreted by the device's operating system and software.

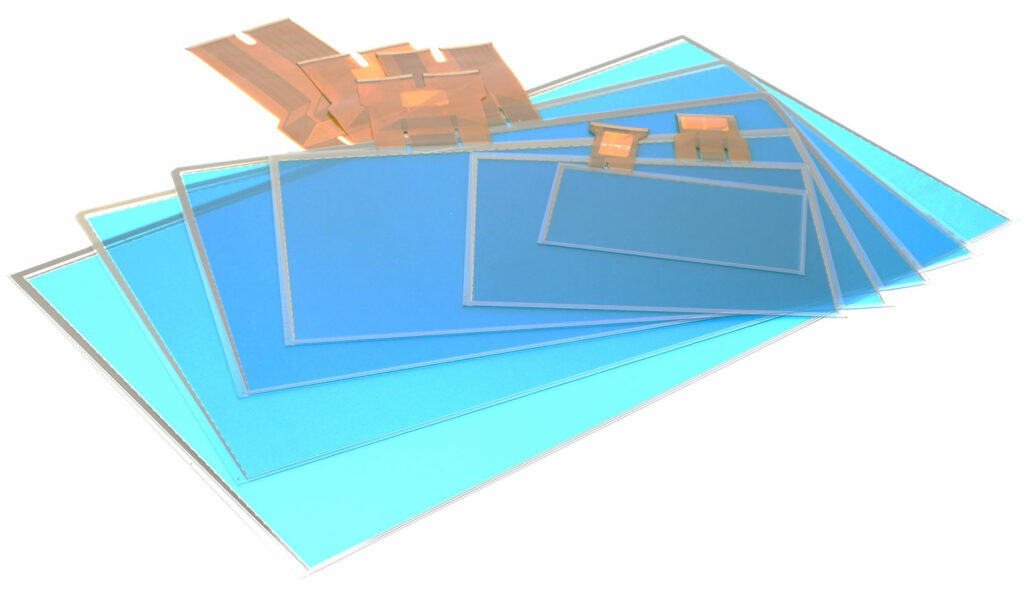
Touch sensors for single touch
The touch sensors in resistive single-touch displays are at the heart of this technology. They consist of two transparent, conductive layers that are separated by small spacers. When touched, the upper layer is pressed onto the lower layer, which generates a voltage at the point of contact. This change is detected by the electronics and recognized as a precise contact point. This simple but effective mode of operation makes resistive touch sensors extremely reliable and versatile, even in difficult environments.

Why EP Electronic Print?
At EP Electronic Print, we rely on state-of-the-art components and technologies to develop innovative and customized HMI solutions.
Do you have any questions or would you like to find out more about our HMI solutions?
Our team will be happy to advise you and work with you to find the best solution for your project. Use our contact form or call us directly - we look forward to hearing from you!
We are here for you
Telefon: +49 (0)8142 /420896-20
E-Mail: projekte@ep-electronicprint.de Allgemeine Anfragen:
Telefon: +49 (0)8142 /420896-0
E-Mail: info@ep-electronicprint.de EP Electronic Print GmbH
Am Weidegrund 8 & 10
82194 Gröbenzell